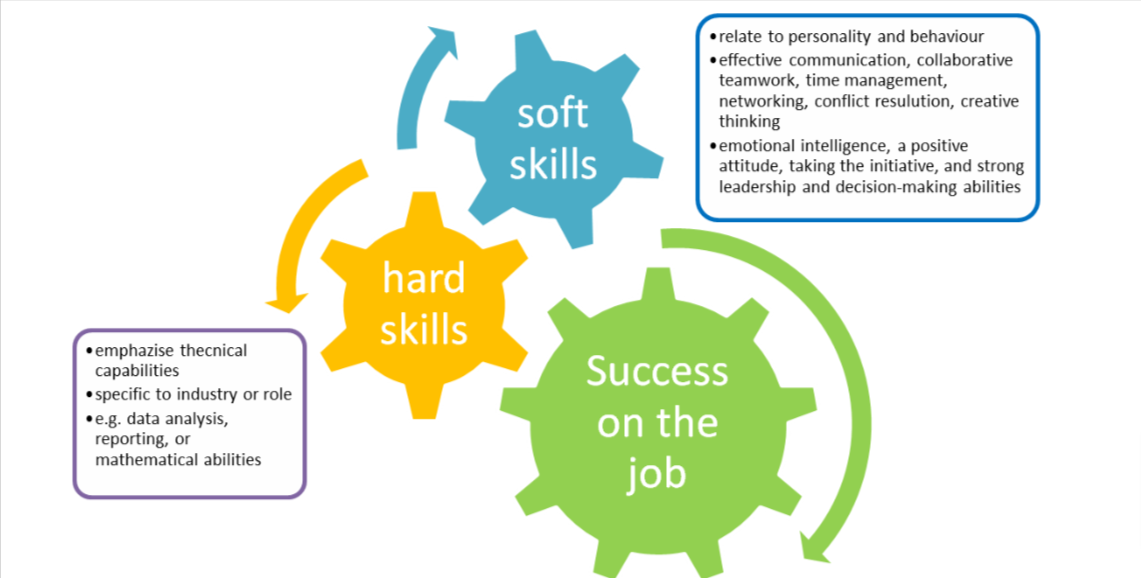
Soft skills are essential personal attributes that contribute to success on the job. These skills include time management, collaborative teamwork, networking, conflict resolution, creative thinking, and effective communication. Apprentices with well-developed soft skills are adaptable, flexible, and can bring significant benefits to their companies.
However, apprentices from disadvantaged backgrounds or with fewer opportunities might not have had the chance to develop these critical skills. Factors such as living in poor conditions or having a disability can hinder their ability to communicate effectively and develop other soft skills, leading to challenges in the work-based learning (WBL) environment.
These obstacles can demotivate learners, making it difficult for them to complete tasks efficiently in the WBL environment. To address these challenges, apprentices from disadvantaged backgrounds need robust support from their mentors. As a mentor, you can design and implement tailored soft skills training programs to help your apprentices improve these essential skills and feel more confident in using them. This, in turn, will motivate them to develop skills they may not have previously considered important.
Soft skills training focuses on abilities such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, in contrast to hard skills that emphasize technical capabilities. Other crucial soft skills include emotional intelligence, a positive attitude, taking Other crucial soft skills include emotional intelligence, a positive attitude, taking the initiative, and strong leadership and decision-making abilities. Despite being often underappreciated in the WBL environment, soft skills are just as important as hard skills.
Unlike hard skills, soft skills are not specific to any industry or role; rather, they relate to personality and behaviour. While hard skills like data analysis, reporting, or mathematical abilities can be taught relatively easily, soft skills training involves teaching new behaviours and ways of thinking, making it more challenging. Moreover, the effectiveness of soft skills training in the WBL environment is less quantitative and harder to measure.
An effective soft skills development plan and its implementation must be adapted to the needs of each apprentice, as every learner has different qualifications and abilities. By focusing on these individual needs, mentors can create a supportive environment that promotes the growth and development of soft skills, enabling apprentices to thrive and contribute positively to their teams.